Wuhan SY Blue Sky Environmental Technology Engineering Co., Ltd.
Service Field
Sewage treatment
Submit
Summarize
Industrial wastewater refers to the waste water, sewage and waste liquid produced in the industrial production process, which contains industrial production materials, intermediate products and products lost with water and pollutants produced in the production process. Our company has developed and treated the following ten categories of industrial wastewater:
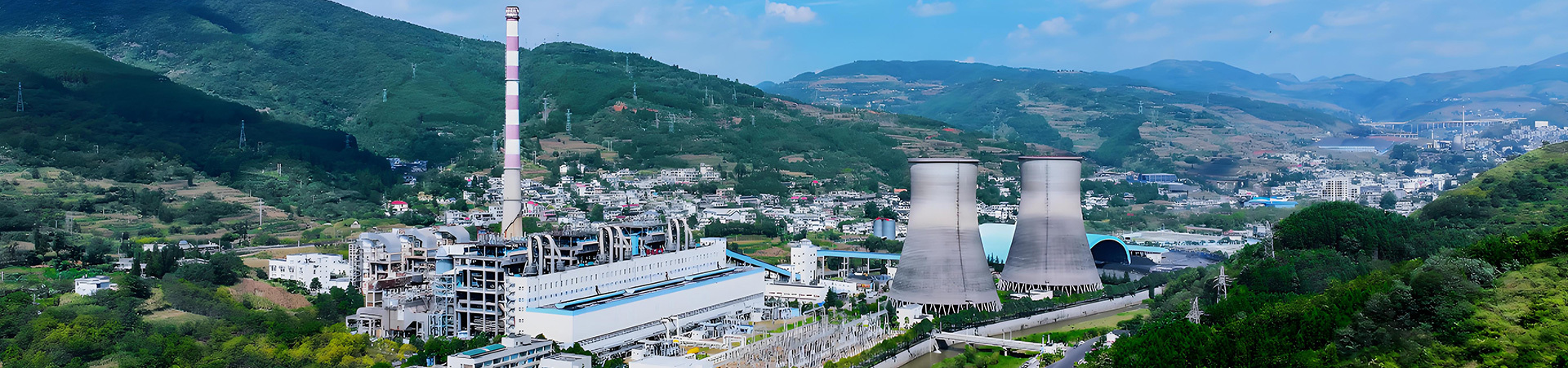
1. Desulfurization wastewater treatment process of coal-fired power plants
Most desulphurization units in power plants adopt flue gas wet desulphurization process. The process is mainly composed of alkaline oxide slurry preparation system, metal salt dehydration system and desulphurization wastewater treatment system. In the process of continuous circulation, the water in the slurry of desulfurization unit will enrich heavy metal elements and Cl-, etc., on the one hand, accelerate the corrosion of desulfurization equipment, on the other hand, affect the quality of metal salts, and need to discharge waste water in time.
Desulfurization wastewater treatment process of power plant: desulfurization wastewater → waste water tank → waste water pump → pH neutralization tank → settling box → flocculation box → clarifier → outlet water tank → outlet water pump → standard discharge
The desulphurization wastewater treatment system includes three parts: wastewater treatment, dosing and sludge treatment. Waste water treatment system is mainly composed of waste water tank, triple header, clarifying tank, mud pump, water tank, clean water pump, fan, dehydrator and other parts of the equipment. In addition to a large number of Cl-, Mg2+ impurities in desulfurization wastewater, also include: fluoride, nitrite and so on; Heavy metal ions, such as Cu2+, Hg2+, etc. Insoluble sulfuric acid compounds and fine dust. In order to meet the wastewater discharge standards, it is necessary to equip the corresponding wastewater treatment equipment.
2. Chemical industry wastewater treatment process
Chemical industry wastewater is mainly from: petrochemical industry, coal chemical industry, acid and alkali industry, fertilizer industry, plastic industry, pharmaceutical industry, dye industry, rubber industry and other discharged production wastewater.
The main measures for the prevention and control of chemical wastewater pollution are as follows: firstly, the production process and equipment should be reformed, pollutants should be reduced, waste water should be prevented from being discharged, and comprehensive utilization and recovery should be carried out; The degree of treatment of the wastewater that must be discharged should be selected according to the water quality and requirements.
Primary treatment mainly separates suspended solids, colloids, oil slicks or heavy oils in water. Methods such as water quality and quantity regulation, natural precipitation, floating and oil separation can be used.
Secondary treatment is mainly to remove biodegradable organic dissolved matter and part of colloids, reduce biochemical oxygen demand and part of chemical oxygen demand in wastewater, usually using biological treatment. After biological treatment, there is still a considerable amount of COD in the wastewater, sometimes with higher color, smell, taste, or because of high environmental health standards, it is necessary to use tertiary treatment methods to further purify.
Tertiary treatment is mainly to remove organic pollutants and dissolved inorganic pollutants that are difficult to biodegrade in wastewater. The commonly used methods are activated carbon adsorption and ozone oxidation, and ion exchange and membrane separation technology can also be used. All kinds of chemical industry wastewater can be selected according to different water quality, water quantity and the requirements of external discharge water quality after treatment.
3. Printing and dyeing industry wastewater treatment process
The printing and dyeing industry uses a large amount of water, usually 100 to 200t of water per printing and dyeing 1t textile processing. 80% to 90% of them are discharged as printing and dyeing wastewater. The common treatment methods are recycling and harmless treatment.
Waste water can be recycled according to the characteristics of water quality, such as bleaching boiling waste water and dyeing printing waste water split, the former can be convection washing. One water multi-purpose, reduce emissions;
Lye recycling, usually using evaporation recovery, such as large amount of lye, can be recovered by three-effect evaporation, small amount of lye, can be recovered by thin film evaporation;
Recovery of dyes. For example, shilin dyes can be acidified into cryptobaric acid, which is a colloidal particle. It is suspended in the residual liquid and recycled after precipitation filtration.
Physical treatment methods include precipitation method and adsorption method. Precipitation method mainly removes suspended solids in wastewater. Adsorption method is mainly to remove dissolved pollutants and decolorization in wastewater.
Chemical treatment methods include neutralization method, coagulation method and oxidation method. The neutralization method is to adjust the pH in the wastewater and reduce the color of the wastewater. The coagulation method is to remove disperse dyes and colloidal substances in wastewater. Oxidation method is to oxidize the reducing substances in the wastewater, so that the sulfide dye and the VAT dye precipitate down.
Biological treatment methods include activated sludge, biological turntable, biological drum and biological contact oxidation method. In order to improve the quality of the effluent, to meet the discharge standards or recycling requirements. A combination of several approaches is often required.
4. Paper industry wastewater treatment process
Papermaking wastewater mainly comes from two production processes of pulping and papermaking in papermaking industry. Pulping is the separation of fibers in plant raw materials to make pulp, and then bleached; Paper making is to dilute, shape, press and dry the stock to make paper. Both processes produce large amounts of wastewater.
The wastewater produced by pulping is the most polluted. When washing the pulp, the wastewater is black brown, called black water, the concentration of pollutants in black water is very high, BOD up to 5-40g /L, containing a lot of fiber, inorganic salts and pigments. The wastewater from the bleaching process also contains a lot of acid and alkali substances. The waste water from the paper machine is called white water, which contains a lot of fibers and fillers and adhesives added during the production process.
The treatment of paper industry wastewater should focus on improving the recycling water rate, reducing water consumption and wastewater discharge, and should also actively explore a variety of reliable, economic and able to make full use of useful resources in wastewater treatment methods. For example, the flotation method can recover fibrous solid substances in white water, the recovery rate can reach 95%, and the clarified water can be reused; The combustion method can recover sodium hydroxide, sodium sulfide, sodium sulfate and other sodium salts combined with organic matter in black water.
Neutralization method to adjust the pH value of wastewater; The suspended solids in wastewater can be removed by coagulation sedimentation or flotation. Chemical precipitation method can decolorize; Biological treatment can remove BOD, which is more effective for kraft paper wastewater. The wet oxidation method is successful in treating sulfite pulp wastewater. In addition, there are also reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, electrodialysis and other treatment methods at home and abroad.
5. Dye production wastewater treatment process
Dye production wastewater contains acids, bases, salts, halogens, hydrocarbons, amines, nitrocompounds and dyes and their intermediates, and some also contain pyridine, cyanogen, phenol, benzidine and heavy metals such as mercury, cadmium, chromium and so on. The wastewater has a complex composition. It is toxic and difficult to handle. So dye production wastewater treatment. It should be based on the characteristics of the wastewater and the requirements for its discharge. Choose appropriate treatment methods.
For example, to remove solid impurities and inorganic substances, coagulation method and filtration method can be used; Chemical oxidation method, biological method and reverse osmosis method are used to remove organic matter and toxic substances. The decolorization process can be composed of coagulation method and adsorption method, and the ion exchange method can be used to remove heavy metals.
6. Food industry wastewater treatment process
The raw materials of food industry are extensive, the products are diverse, and the amount and quality of wastewater are very different.
The main pollutants in wastewater are:
Solid substances floating in wastewater, such as vegetable leaves, fruit peels, minced meat, bird feathers, etc.; The substances suspended in the wastewater include grease, protein, starch, colloidal substances, etc. Acid, alkali, salt, sugar, etc., dissolved in wastewater; Mud sand and other organic matter carried by raw materials; Pathogenic bacteria and poisons.
Food industry wastewater is characterized by high content of organic matter and suspended matter, easy to corrupt, generally no large toxicity. Its harm is mainly to make the water eutrophication, resulting in the death of aquatic animals and fish, and promote the organic matter deposited on the bottom to produce odor, deteriorate the water quality and pollute the environment.
In addition to proper pretreatment according to the characteristics of water quality, biological treatment is generally suitable for the treatment of food industry wastewater. If the effluent quality is very high or the organic content in the wastewater is very high, a two-stage aeration tank or a two-stage biological filter can be used, or a multi-stage biological turntable. Or combined use of two biological treatment devices, can also be used anaerobic - aerobic series.
7. Heavy metal wastewater treatment technology
Heavy metal wastewater mainly comes from the wastewater discharged by mining, smelting, electrolysis, electroplating, pesticide, medicine, paint, pigment and other enterprises. The types, contents and forms of heavy metals in wastewater vary with different production enterprises.
The principles of heavy metal wastewater treatment are:
The most fundamental is to reform the production process, do not use or less toxic heavy metals; The second is to adopt reasonable process flow, scientific management and operation, reduce the amount of heavy metals and the amount of waste water lost, and minimize the amount of wastewater discharged. Heavy metal wastewater should be treated in situ at the production site and not mixed with other wastewater to avoid complicating treatment. It should not be discharged directly into urban sewers without treatment, so as not to expand heavy metal pollution.
The treatment of heavy metal wastewater can usually be divided into two categories:
The first is to transform the dissolved heavy metals in the wastewater into insoluble metal compounds or elements, which are removed from the wastewater by precipitation and floating. Applicable methods such as neutralization precipitation method, sulfide precipitation method, floating separation method, electrolytic precipitation (or floating) method, diaphragm electrolysis method;
The second is to concentrate and separate heavy metals in wastewater without changing their chemical forms, which can be used by reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, evaporation and ion exchange. These methods should be used individually or in combination according to the quality and quantity of wastewater.
8. Metallurgical wastewater treatment process
The main characteristics of metallurgical wastewater are large amount of water, variety and complex and changeable water quality. According to the source and characteristics of wastewater classification, there are mainly cooling water, pickling wastewater, washing wastewater (dust removal, gas or flue gas), slag wastewater, coking wastewater and condensed, separated or spilled wastewater by production.
The development trend of metallurgical wastewater treatment is:
Develop and adopt new processes and technologies with no or less water use and no pollution or less pollution, such as quenching coke by dry method, preheating coking coal, desulfurization and decyanation from coke oven gas, etc. Developing comprehensive utilization technologies, such as the recovery of useful substances and heat from waste water and gas, to reduce the loss of materials and fuels; According to different water quality requirements, comprehensive balance, stream use, while improving water quality stability measures, and constantly improve the recycling rate of water;
Develop new treatment processes and technologies suitable for the characteristics of metallurgical wastewater, such as magnetic treatment of steel wastewater. It has the advantages of high efficiency, less footprint, convenient operation and management.
9. Acid and alkali wastewater treatment technology
Acidic wastewater mainly comes from steel plants, chemical plants, dye plants, electroplating plants and mines, which contain various harmful substances or heavy metal salts. The mass fraction of acids varies widely, from less than 1% for the low to more than 10% for the high.
Alkaline wastewater mainly comes from printing and dyeing plants, tanneries, paper mills, oil refineries and so on. Some of them contain organic or inorganic bases. The mass fraction of the base is higher than 5% and less than 1%. Acid and alkali wastewater, in addition to containing acid and alkali, often contains acid salt, basic salt and other inorganic and organic matter.
Acid and alkali wastewater has strong corrosiveness and can be discharged only after proper treatment.
One principle of treating acid and alkali wastewater is:
High concentration of acid and alkali wastewater, should give priority to recycling, according to the water quality, water quantity and different process requirements, plant or regional scheduling, as far as possible to reuse: if it is difficult to reuse, or the concentration is low, the amount of water is large, can use concentrated method to recover acid and alkali.
Low concentration of acid and alkali wastewater, such as pickling tank cleaning water, alkali tank rinsing water, should be neutralized.
For neutralization, the principle of treating waste with waste should be considered first. For example, acid and alkali wastewater neutralize each other or use waste alkali (slag) to neutralize acidic wastewater, and use waste acid to neutralize alkaline wastewater. In the absence of these conditions, a neutralizer can be used.
10. Beneficiation wastewater treatment process
Mineral processing wastewater has the characteristics of large amount of water, high content of suspended matter and many kinds of harmful substances. The harmful substances are heavy metal ions and mineral processing agents. Heavy metal ions are copper, zinc, lead, nickel, barium, cadmium and arsenic and rare elements.
Flotation agents added in the beneficiation process have the following categories: collector. Such as RocssMe, black drug [(RO)2PSSMe], white drug [CS(NHC6H5)2]; Inhibitor, such as cyanide salt (KCN, NaCN), water glass (Na2SiO3); Foaming agents, such as turpentine, cresol (C6H4CH30H); Active punishment, such as copper sulfate (CuS04), heavy metal salts; Vulcanizing agents, such as sodium sulfide; Paddle conditioner, such as sulfuric acid, lime, etc.
The mineral processing wastewater can be effectively removed by tailings dam, and the content of heavy metals and flotation agents can also be reduced. If the emission requirements are not met, further treatment should be carried out. The commonly used treatment methods are:
Lime neutralization method and calcined dolomite adsorption method can be used to remove heavy metals. The main flotation reagents can be used by ore adsorption and activated carbon adsorption. Cyanide-containing wastewater can be chemically oxidized.
Inquire
Leave a message and you will receive a surprise gift!
Head Office Address: No. 1178, Gaoke Building, Jiayuan Road, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei, China
WhatsApp/Mobile: +86-13801339781
Factory Address: No. 283 Zhongshan Avenue, Jinshan Street Office, Huangshi Economic Development Zone, Hubei, China